The following programs were solved by various friends. Hence if there are any mistakes/bugs/errors in the program kindly comment on at the end of the Post. We will try to rectify it. For downloading all the programs in a single PDF file: click this link https://engineeringcourses.files.wordpress.com/2010/12/clip_image022_thumb1.jpg2010/12/c-programming-assignments-with-answers-21-questions.html
Question 1
The straight line method of computing the yearly depreciation of the value of an item is given by
Depreciation = (Purchase Price – Salvage Value) / years of service.
Write a program to determine the salvage value of an item when the purchase price, years of service and the annual depreciation are given.
|
Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int yr; float price,dep,salvalue; printf("enter the purchase price,years of service, annual depreciation"); scanf(" %f %d %f", &price,&yr,&dep); salvalue = price-(dep*yr); printf("The salvage value of the item is %f",salvalue); getch(); return 0; } Output: enter the purchase price, years of service, annual depreciation 5000 8 5.25 The salvage value of the item is 4958.000000 |
Question 2
Write a function exchange to interchange the values of two variables, say x and y. Illustrate the use of this function, in a calling function. Make x and y as global variables.
|
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void exchange(int a,int b); void exchange(int a,int b) {int c; c=a; a=b; b=c; printf("the I no is …….%d \n the second no. is…….%d",a,b); } int main() {int x,y; printf("enter two no’s…..\n first no is…\n"); scanf("%d",&x); printf("enter second number….."); scanf("%d",&y); exchange(x,y); getch(); return 0; }
Output: enter two no’s….. first no is… 5 enter second number…..9 the I no is …….9 the second no. is…….5
|
Question 3
Write a function space(x) that can be used to provide a space of x positions between two output numbers.
|
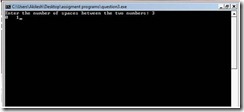
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> / /The two output numbers here are 0 and 1 void space(int); int main() { int x; printf("Enter the number of spaces between the two numbers: "); scanf("%d", &x); space(x); getch(); return 0; } void space(int x) { int i; printf("0"); for(i=0;i<x;i++) printf(" "); printf("1"); } Output: |
Question 4
Write a function prime that returns 1 if its argument is a prime number and returns zero otherwise.
|
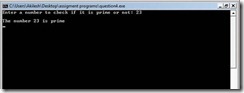
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int prime(int); int main() { int res,num; printf("Enter a number to check if it is prime or not: "); scanf("%d", &num); res=prime(num); if(res==1) printf("\nThe number %d is prime\n", num); if(res==0) printf("\nThe number %d is not prime\n", num); getch(); return 0; } int prime(int n) { int i; for(i=2;i<=n/2;i++) {if(n%i==0) return 0;} return 1; }
Output: |
Question 5
Where u is the initial velocity (m/s), a the acceleration due to gravity (m/s2). Write a program to evaluate the distance travelled at regular intervals of time, given the values of u and a. the program should provide the flexibility to the user to select his own time intervals and repeat the calculations of different values of u and a
|
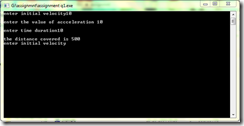
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int s=0,d,u,a,t; while (1) { printf("\nenter initial velocity"); scanf("%d",&u); printf("\nenter the value of accceleration "); scanf("%d",&a); printf("\nenter time duration"); scanf("%d",&t); d = (a*t*t)/2; s=u+d; printf("\nthe distance covered is %d\n",d); } getch(); }
Output: |
Question 6
Write a program using for loops to produce a triangle using the asterisk (*) symbol. The program should prompt the user for the height of the triangle and check to see that the user entered a number greater than or equal to 3 and less than or equal to 40. If the user enters an invalid number, the program will print an error message and exit. If the user enters a valid number the program will print an equilateral triangle of height n, where n is the number the user entered at the console. The program should be written using no more than three printf() statements.
|
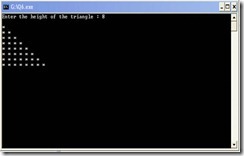
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int i, j, h; printf("Enter the height of the triangle : "); scanf("%d",&h); if((h>=3)&&(h<=40)) { for(i=1; i<=h; i++) { printf("\n"); for(j=1; j<=i; j++) { printf("* "); } } } else printf("\n\n\n\nError…..!!!!\n\n\n\nPress any key to exit…"); getch(); return 0; }
OUTPUT SCREEN
|
Question 7
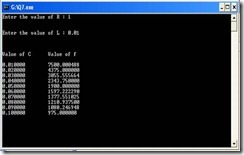
For an certain electrical circuit with an inductance L and resistance R, the damped natural frequency is given by
√(1/LC – R2/4C2). It is desired to study the variation of this frequency with C (capacitance). Write a program to calculate the frequency for different values of C starting from 0.01 to 0.1 in steps of 0.01.
|
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { float C[10] = { 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.10 }; float R, L, f[10]; int i; printf("Enter the value of R : "); scanf("%f",&R); printf("\n\nEnter the value of L : "); scanf("%f",&L); for(i=0; i<10; i++) { f[i] = sqrt(1/(L*C[i])-(R*R)/(4*C[i]*C[i])); } printf("\n\n\nValue of C\tValue of f\n\n"); for(i=0; i<10; i++) { printf("%f\t%f\n",C[i],f[i]); } getch(); return 0; }
OUTPUT SCREEN
|
Question 8
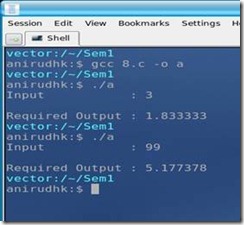
Write a program to determine and print the sum of the following harmonic series for a given value of n:
1 + ½ + 1/3 + ¼ +….. +1/n
The value of n should be given interactively through the terminal
|
Program: #include <stdio.h> int main() { int n; float a,i; printf("Input \t\t: "); scanf("%d", &n); while (!(n>0)) { printf("\n\nEnter a POSITIVE Number : "); scanf("%d", &n); }
for (i=1; i<=n; i++) { a += (1.0/i); } printf("\nRequired Output : %f\n", a); return 1; } Output: |
Question 9
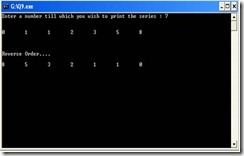
Write a program that prompts the user for the number of Fibonacci numbers to generate and then prints the Fibonacci numbers to the screen. The user will enter some number, which we’ll call n. Your program should use a for loop to generate the Fibonacci numbers up to n, and then use a while loop to generate the numbers from n back down to zero.
|
#include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> int main() { int i, n , fb[100]; fb[0]=0; fb[1]=1; printf("Enter a number till which you wish to print the series : "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n\n"); for(i=2; i<n; i++) { fb[i]=fb[i-1]+fb[i-2]; } for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("%d\t",fb[i]); } printf("\n\n\n\nReverse Order….\n\n"); i=n-1; while(i>=0) { printf("%d\t",fb[i]); i–; } getch(); return 0; }
OUTPUT SCREEN |
Question 10
Write a program to read the price of an item in decimal form (Eg 18.75) and print the output in paise like (1875).
|
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { printf("\t\t\t\t Program No. 10\n"); float rs,pais; printf("Enter the price of an item in rupees\n"); scanf("%f",&rs); pais = rs*100; printf("The price in paise is : %7.0f",pais); getch(); return 0; } Output: Program No. 10 Enter the price of item in rupees 187.5 The price in paise in : 18750 |
Question 11
A cloth showroom has announced the following seasonal discounts on purchase of items
|
Purchase Amount |
Discount |
|
|
Mill Cloth |
Handloom Items |
|
|
0-100 |
– |
5% |
|
101-200 |
5% |
7.5% |
|
201-300 |
7.5% |
10.0% |
|
301 and above |
10% |
15.0% |
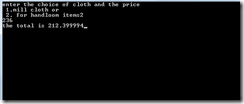
Write a program using switch and if statement to compute the net amount paid by a customer.
|
Program: #include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h>
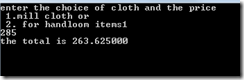
int main() { int choice; float price,total; printf("enter the choice of cloth and the price \n 1.mill cloth or \n 2. for handloom items"); scanf("%d %f",&choice,&price); switch(choice) { case 1:if (price>=0 && price<=100) total=price; else if (price>=101 && price<=200) total=price-(0.05*price); else if (price>=201 && price<=300) total=price-(0.075*price); else if (price>=301) total=price-(0.10*price); break; case 2:if (price>=0 && price<=100) total=price-(0.05*price); else if (price>=101 && price<=200) total=price-(0.075*price); else if (price>=201 && price<=300) total=price-(0.1*price); else if (price>=301) total=price-(0.15*price); break;} printf("the total is %f",total); getch(); return 0; } Output: |
Question 12
Write a program that will read the value of x and evaluate the following function.
Y=1 for x >0
Y=0 for x=0
Y=-1 for x< 0
Using (a) nested if statements (b) else if statements (c) conditional Operator
|
Program: #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> int main() { float x,y; printf("Enter thhe value of X="); scanf("%f",&x); if (x>0) printf("Y=1"); else if (x==0) printf("Y=0"); else if(x<0) printf("Y=-1"); getch(); return 0; } Output: Enter the value of X=6 Y=1 |
Question 13
A number is special if it is divisible by 15. A number is big if it is greater than 999. A number is weird if it is divisible by 5 and 6 but not 18. A number is scary if it is big or weird. Declare four variables called special, big, weird and scary and make suitable assignments to these variables as a number is tested.
|
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int n,special,big,weird,scary; printf("enter a no."); scanf("%d",&n); if(n%15==0) { special=n; printf("%d is a special no\n",special); }
if (n>999) { big=n; printf("%d is a big no\n",big); } if(n%5==0 && n%6==0 && n%18!=0) { weird=n; printf("%d is a weird no.\n",weird); } if(n==big || n==weird) { scary=n; printf("%d is a scary no\n",scary); } getch(); return 0; }
Output: Enter a no. 1500 1500 is a special no 1500 is a big no 1500 is a weird no 1500 is a scary no
|
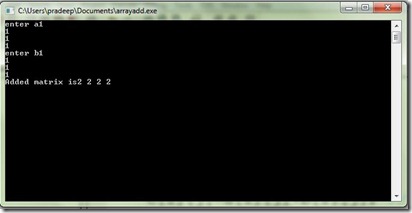
Question 14
Declare two arrays A and B, find A n B and A u B.
|
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() {int n; printf("enter the size of the array"); scanf("%d",&n); int a[n],b[n]; printf("enter elements of I array"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {scanf("%d",&a[i]);} printf("enter elements of II array"); for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {scanf("%d",&b[j]);} printf("the intersection of two arrays are"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {if(a[i]==b[j]){printf("%d",b[j]); }}} printf("\n"); printf("the union of two arrays is\n"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d",a[i]); }
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{int var=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(b[j]==a[i]) {var=var+1;} } if(var==0) {printf("%d",b[j]);} }
getch(); return 0; }
Output: enter the size of the arrays 5 enter elements of I array 7 8 9 5 4 enter elements of II array 8 9 2 3 6 the intersection of two arrays are89 the union of two arrays is 78954236 |
Question 15
Write a program to, reverse a given array
|
Program: #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> int main() { int n,p; printf("Enter size of array \n"); scanf("%d", &n); int a[n],i,t; printf("Enter elements of array \n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); i=0; p=n; while(i<=n/2) { t=a[i]; a[i]=a[n-1]; a[n-1]=t; i++; n–; } printf("Reversed array \n"); for(i=0;i<p;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); getch(); return 0; } Output: Enter the size of array4 Enter elements of array1 3 7 4 Reversed array 4 7 3 1 |
Question 16
Search an element in an array and display the index position of all the elements of that value.
|
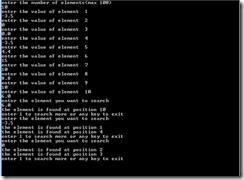
Program:- #include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> int main() { int i,n=0,ans=0,s=0; double a[100],ele; char t; while(n<=0||n>100) { printf("enter the number of elements(max 100)\n"); scanf("%d",&n); } for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("enter the value of element"); printf(" %d\n",i+1); scanf("%lf",&a[i]); } do { printf("enter the element you want to search\n"); scanf("%lf",&ele); s=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(a[i]==ele) {printf("the element is found at position %d\n",i+1); s+=1;} } if(s==0) { printf("the element is not found\n"); } printf("enter 1 to search more or any key to exit\n"); t=getch(); ans = t-48; }while(ans==1); return 0; }
Output:
|
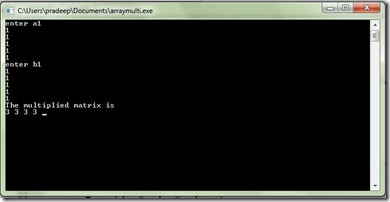
Question 17
Perform the matrix multiplication using two dimensional array by sending entire array to a function mmultiply()
|
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void multiply(int a[][],int b[][]); int main() { int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3]; int i,j;
printf("matrix a:"); for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++} scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } printf("matrix b:"); for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++} scanf("%d",&b[i][j]); } multiply(a[][],b[][]); getch(); return 0; }
void multiply(int a[][],int b[][]) { int i,j,k; for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++) { c[i][j]=0; for(k=0;k<n;k++) { c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j]; } } } printf("resultant matrix:"); for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++} scanf("%d",&c[i][j]); } }
OUTPUT:- Matrix a:0 1 2 2 3 4 3 4 5 Matrix b:0 1 2 2 3 4 3 4 5 Resultant matrix:6 13 16 18 31 40 23 40 52 |
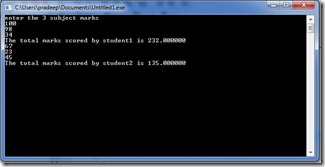
Question 18
Write a program to calculate the standard deviation of an array of values. The array elements are read from the terminal. Use functions to calculate standard deviation and mean.
|
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> int main() { int n; printf("Enter how many numbers you want to enter?"); scanf("%d",&n); int a[n]; printf("enter the numbers"); double x=0.0,x1=0.0; int i; double z; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); x=x+a[i]; } x=x/n; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { x1=x1+pow((x-a[i]),2); } z=sqrt(x1/n); printf("standard deviation is %f",z); getch(); return 0; } |
Question 19
An election is contested by 5 candidates. The candidates are numbered 1 to 5 and the voting is done by marking the candidate number on the ballot paper. Write a program to read the ballots and count the votes cast for each candidate using an array variable count. In case, a number read is outside the range 1 to 5, the ballot should be considered as a spoilt ballot and the program should also count the number of spoilt ballots.
|
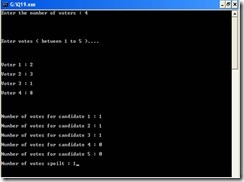
#include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> int main() { int i, vote[100], c1=0, c2=0, c3=0, c4=0, c5=0, c_spoilt=0, n; printf("Enter the number of voters : "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n\n\n\n\nEnter votes ( between 1 to 5 )….\n\n\n\n"); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("\nVoter %d : ",i+1); scanf("%d", &vote[i]); if((vote[i]<=5)&&(vote[i]>=1)) { switch(vote[i]) { case 1 : c1++; break; case 2 : c2++; break; case 3 : c3++; break; case 4 : c4++; break; case 5 : c5++; break; default : printf("Error…!!!"); } } else { vote[i]=0; c_spoilt++; } } printf("\n\n\n\nNumber of votes for candidate 1 : %d", c1); printf("\n\nNumber of votes for candidate 2 : %d",c2); printf("\n\nNumber of votes for candidate 3 : %d",c3); printf("\n\nNumber of votes for candidate 4 : %d",c4); printf("\n\nNumber of votes for candidate 5 : %d",c5); printf("\n\nNumber of votes spoilt : %d",c_spoilt); getch(); return 0; }
OUTPUT SCREEN |
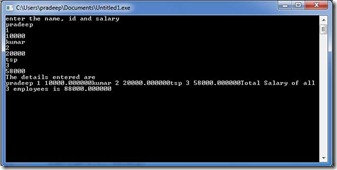
Question 20
Define a structure called cricket that will describe the following information:
Player name, team name, batting average.
Using cricket, declare an array player with 10 elements and write a program to read the information about all the 50 players and print a team wise list containing names of players with their batting average.
|
Program: #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h>
struct cricket { char playername[50]; char teamname[50]; float battingavg; }; int main() { struct cricket player[100]; int i,n,m,j; char name[10][10]; printf("Enter the no. of teams:- "); scanf("%d",&n); for(j=0;j<n;j++) { printf("Enter the name of the teams:- "); scanf("%s",&name[j]); } printf("\nEnter the no. of players:- "); scanf("%d",&m); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { printf("Enter the %d player name, team name & batting avg:- ",i+1); scanf("%s%s%f",&player[i].playername,&player[i].teamname,&player[i].battingavg); } printf("\n\nListing according to team names::\n"); for(j=0;j<n;j++) { printf("\n%s-\n",name[j]); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { if(strcmp(player[i].teamname,name[j])==0) { printf("\t%s\t%f\n",player[i].playername,player[i].battingavg); } } } getch(); return 0; }
Output: Enter the no. of teams:- 2 Enter the name of the teams:- TEAM1 Enter the name of the teams:- TEAM2
Enter the no. of players:- 4 Enter the 1 player name, team name & batting avg:- A TEAM1 41 Enter the 2 player name, team name & batting avg:- B TEAM2 23 Enter the 3 player name, team name & batting avg:- C TEAM1 15 Enter the 4 player name, team name & batting avg:- D TEAM2 45
Listing according to team names::
TEAM1- A 41.000000 C 15.000000
TEAM2- B 23.000000 D 45.000000
|
Question 21
A bookshop uses a personal computer to maintain the inventory of books that are being sold at the shop. The list includes details such as author, title, isbn number, price, author, stock position. Whenever a customer wants a book, the shopkeeper inputs the title or isbn number and the system replies whether the book is available or not. If it is not, an appropriate message is displayed. If book is in the list, then the system displays the book details and asks for number of copies. If the requested copies are available, the total cost of the books is displayed, otherwise the message “Requested copies are not in stock” is displayed. Implement using structures.
|
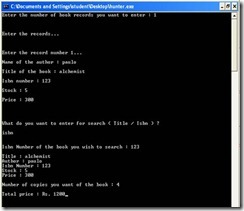
#include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> struct book { char author[50]; char title[50]; int isbn_num, stock, price; }; int main() { char search[20]; char t1[50]; int i, n, n1, copies, bill; struct book b1[100]; printf("Enter the number of book records you want to enter : "); scanf("%d", &n); printf("\n\n\nEnter the records…\n\n\n"); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { printf("\nEnter the record number %d…\n",i+1); printf("\nName of the author : "); gets(b1[i].author); printf("\nTitle of the book : "); gets(b1[i].title); printf("\nIsbn number : "); scanf("%d", &b1[i].isbn_num); printf("\nStock : "); scanf("%d", &b1[i].stock); printf("\nPrice : "); scanf("%d", &b1[i].price); } printf("\n\n\n\nWhat do you want to enter for search ( Title / Isbn ) ?\n\n"); scanf("%s",search); if(strcmpi("title",search)==0) { printf("\n\nTitle of the book you wish to search : "); gets(t1); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { if( { printf("\nTitle : "); puts(b1[i].title); printf("\nAuthor : "); puts(b1[i].author); printf("\nIsbn Number : %d",b1[i].isbn_num); printf("\nStock : %d",b1[i].stock); printf("\nPrice : %d",b1[i].price); printf("\n\nNumber of copies you want of the book : "); scanf("%d",&copies); if(copies<=b1[i].stock) { bill = copies*b1[i].price; printf("\nTotal price : Rs. %d", bill); } else printf("\n\nRequested copies are not in stock…!!!"); } else printf("\n\nRequested book not available…!!!"); } } else if(strcmpi("isbn",search)==0) { printf("\n\nIsbn Number of the book you wish to search : "); scanf("%d",&n1); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { if(b1[i].isbn_num==n1) { printf("\nTitle : %s", b1[i].title); printf("\nAuthor : %s", b1[i].author); printf("\nIsbn Number : %d",b1[i].isbn_num); printf("\nStock : %d",b1[i].stock); printf("\nPrice : %d",b1[i].price); printf("\n\nNumber of copies you want of the book : "); scanf("%d",&copies); if(copies<=b1[i].stock) { bill = copies*b1[i].price; printf("\nTotal price : Rs. %d", bill); } else printf("\n\nRequested copies are not in stock…!!!");
} else printf("\n\nRequested book not available…!!!"); } } getch(); return 0; } OUTPUT SCREEN |